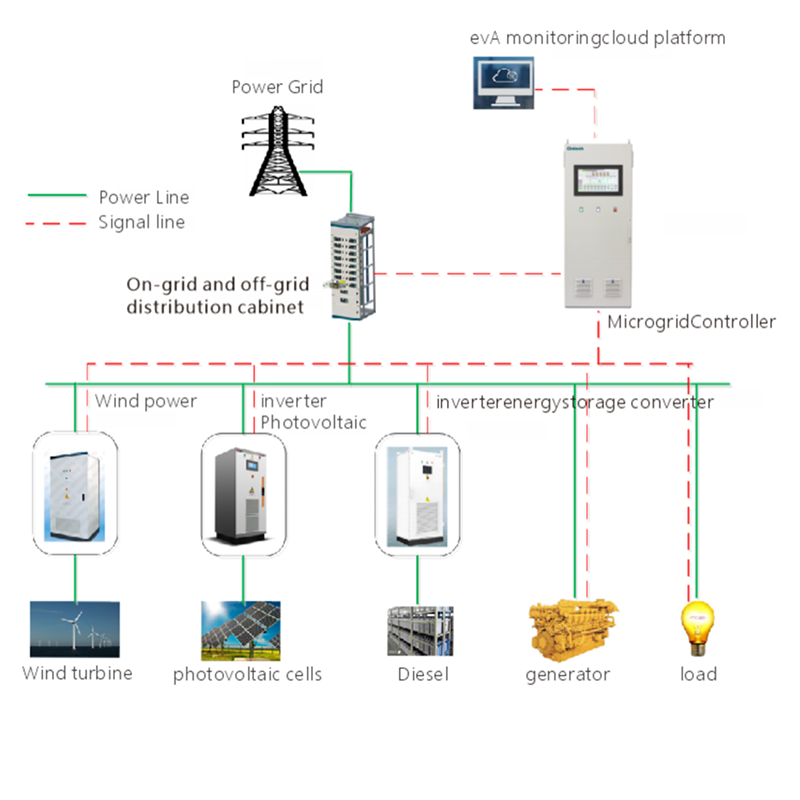
An electrical module is an independent functional unit composed of electrical components, typically designed to perform specific electrical functions such as power management, signal processing, control, or communication. These modules are widely used in various fields, including industrial automation, power systems, consumer electronics, and automotive electronics.

Key aspects of electrical module design
Standardization: Ensuring that modules meet industry standards for compatibility and interchangeability, which simplifies integration and maintenance.
Modularization: Designing modules to be easily replaceable and upgradable, allowing for flexible system configurations and easier troubleshooting.
Integration: Combining multiple functionalities into a single unit to reduce complexity, improve reliability, and enhance overall system performance.
Main Types of Electrical Modules
Power Modules:Description: Provide stable voltage and current outputs. Common types include AC-DC converters, DC-DC converters, and linear regulators.
Applications: Industrial equipment, communication devices, consumer electronics.
Control Modules:Description: Used to control the operation of electrical devices or systems, such as PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers), motor controllers, etc.
Applications: Automated production lines, robotics, smart homes.
Communication Modules:Description: Facilitate data transmission between devices, including wired communication (e.g., RS485, CAN bus) and wireless communication (e.g., Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, ZigBee).
Applications: Internet of Things (IoT), smart grids, vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communications.
Signal Processing Modules:Description: Involve the acquisition, amplification, filtering, or conversion of sensor signals, such as ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converters), DAC (Digital-to-Analog Converters) modules.
Applications: Medical devices, instrumentation, audio equipment.
Protection Modules:Description: Provide protection against overvoltage, overcurrent, short circuits, etc., including fuses, relays, surge protectors.
Applications: Power systems, household appliances, industrial equipment.
Drive Modules:Description: Used to drive motors, relays, or other loads, such as motor driver modules, LED driver modules.
Applications: Electric vehicles, industrial robots, lighting systems.
Sensor Modules:Description: Integrate sensors with signal processing circuits to detect physical quantities like temperature, humidity, pressure, and light.
Applications: Environmental monitoring, smart homes, industrial automation.
Application Areas of Electrical Modules
Industrial Automation:
Usage: Employed in PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers), servo drives, sensors, and other devices to achieve automated control of production lines.
Examples: Assembly lines, robotic arms, conveyor systems.
Power Systems:
Usage: Utilized in distribution cabinets, substations, smart meters, etc., for energy management and protection.
Examples: Power distribution networks, renewable energy integration, fault detection and isolation systems.
Consumer Electronics:
Usage: Integrated into smartphones, home appliances, wearable devices, etc., providing power management and signal processing functionalities.
Examples: Battery management systems in smartphones, energy-efficient appliances, fitness trackers.
Automotive Electronics:
Usage: Applied in electric vehicles, infotainment systems, ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems), and more.
Examples: Electric vehicle battery management, in-car navigation systems, collision avoidance systems.
Internet of Things (IoT):
Usage: Deployed in smart homes, smart cities, environmental monitoring, and other applications to enable device interconnectivity and data transmission.
Examples: Smart thermostats, connected streetlights, air quality monitoring systems.
Detailed Examples:
Industrial Automation:
PLCs: Control complex manufacturing processes with precision and reliability.
Servo Drives: Provide precise motion control for robotics and automation equipment.
Sensors: Monitor various parameters like temperature, pressure, and position to ensure optimal operation.
Power Systems:
Distribution Cabinets: Manage the distribution of electricity within facilities.
Substations: Convert high voltage to lower voltages suitable for end-users.
Smart Meters: Enable remote monitoring and billing of electricity usage.
Consumer Electronics:
Smartphones: Efficient power management ensures longer battery life and better performance.
Home Appliances: Energy-efficient designs reduce power consumption and improve user experience.
Wearable Devices: Compact modules provide essential functions while maintaining small form factors.
Automotive Electronics:
Electric Vehicles: Battery management systems optimize charging and discharging cycles.
Infotainment Systems: Provide multimedia entertainment and navigation services.
ADAS: Enhance safety through features like lane-keeping assist and adaptive cruise control.
Internet of Things (IoT):
Smart Homes: Devices like smart thermostats and lighting systems enhance comfort and energy efficiency.
Smart Cities: Connected infrastructure improves public services and resource management.
Environmental Monitoring: Sensors track air and water quality, helping to maintain a healthy environment.
Conclusion
Electrical modules are essential components of modern electrical systems, characterized by their modularity, standardization, and high efficiency. As technology advances, these modules are evolving towards smarter, more compact, and environmentally friendly designs, providing increasingly efficient and reliable solutions across various industries.