An Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) is a device that provides backup power to electrical equipment during power outages or fluctuations. It ensures that connected devices continue to operate without interruption, protecting them from data loss, hardware damage, or downtime. In this article, we will explore the definition of uninterrupted power, its significance, and how it can be achieved in various settings.

Understanding Uninterrupted Power
Uninterrupted Power, often referred to as an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS), is a system designed to provide emergency power to a load when the primary power source fails. The primary purpose of a UPS is to ensure that critical equipment continues to operate without interruption, even during a power outage.
Key Features of a UPS:
- Backup Power: Provides temporary power during outages, allowing time to save work or shut down equipment properly.
- Voltage Regulation: Protects against power surges, sags, and fluctuations.
- Battery Backup: Uses internal batteries to supply power when the main power source fails.
- Automatic Switchover: Instantly switches to battery power when an outage is detected.
- Runtime: The duration a UPS can power connected devices, depending on battery capacity and load.
Types of UPS Systems:
- Standby (Offline) UPS: Basic and cost-effective, it switches to battery power during outages.
- Line-Interactive UPS: Adjusts voltage fluctuations without switching to battery power, offering better protection.
- Online (Double-Conversion) UPS: Continuously powers devices from the battery, providing the highest level of protection.
Here are the application scenarios
- Standby (Offline) UPS: Suitable for homes and small offices, protecting low-power devices. It offers basic power protection at an affordable price.
- Line-Interactive UPS: Ideal for small to medium-sized businesses, safeguarding servers and network equipment. This type provides a higher level of protection and voltage regulation compared to standby UPSs.
- Online (Double Conversion) UPS: This type is best for data centers and industrial and medical fields, where critical equipment needs maximum protection. It ensures the highest level of power protection by continuously converting power from AC to DC and back to AC. When choosing a UPS, consider the specific needs of your equipment and budget constraints to select the most appropriate type.

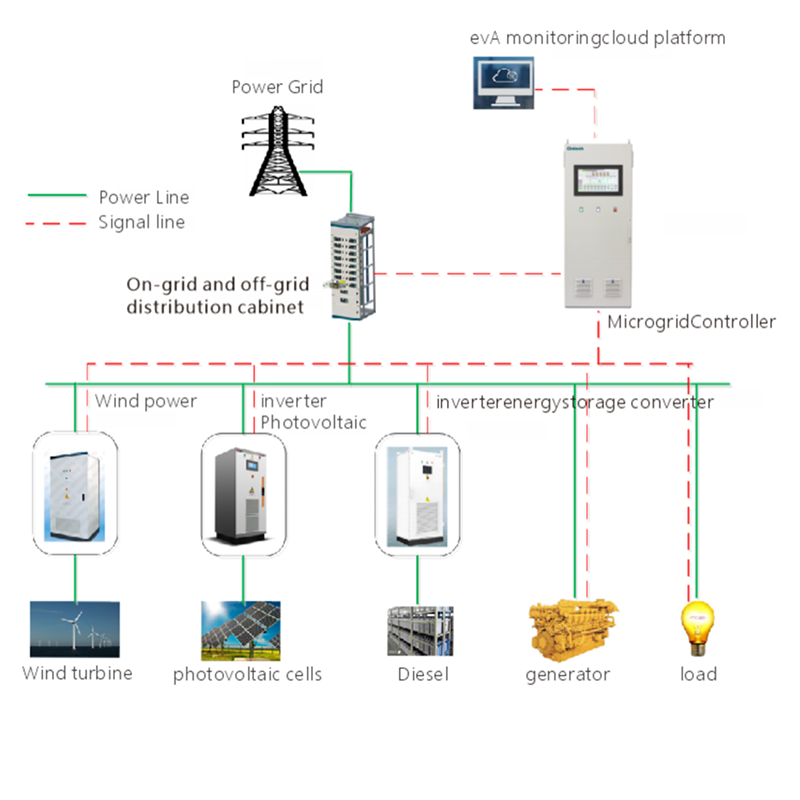
Application Scope of Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS)
The application scope of Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) systems is broad and diverse, covering a wide range of industries and scenarios where continuous power supply and protection against electrical disturbances are critical. Here’s an overview of the primary application areas:
- Data Centers
Purpose: Ensure continuous operation of servers, storage devices, and network infrastructure.
Benefits: Prevents data loss, ensures service availability, and protects against hardware damage due to power outages or voltage fluctuations.
- Healthcare Facilities
Purpose: Supports life-support systems, diagnostic equipment, and other critical medical devices.
Benefits: Guarantees uninterrupted patient care and operational continuity, which is crucial in emergencies.
- Telecommunications Networks
Purpose: Provides backup power for communication infrastructure, including routers, switches, and base stations.
Benefits: Ensures reliability and uptime of voice and data networks, preventing service disruptions.
- Industrial Automation
Purpose: Protect programmable logic controllers (PLCs), robotic systems, and automated manufacturing lines.
Benefits: Minimizes production downtime and prevents loss of control over industrial processes during power interruptions.
- Financial Institutions
Purpose: Safeguarding banking systems, ATMs, and trading platforms.
Benefits: Ensures transaction integrity and continuous operation, which is vital for maintaining customer trust and compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Retail and Point of Sale Systems
Purpose: Keep cash registers, barcode scanners, and electronic payment systems operational.
Benefits: Avoids sales disruptions and ensures smooth business operations even during power outages.
- Home and Office Environments
Purpose: Protects personal computers, printers, and other office equipment from power surges and outages.
Benefits: Prevents data loss and extends the lifespan of sensitive electronics by providing stable power.
- Security Systems
Purpose: Supports surveillance cameras, alarm systems, and access control devices.
Benefits: Maintains security coverage and operational integrity, ensuring that safety measures remain effective during power failures.
In summary
UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) is not only a critical tool for handling unexpected power outages but also a foundational element in ensuring the normal operation of key equipment and systems. By providing stable power support and protection, UPS systems play an indispensable role across various industries, helping businesses and institutions avoid potential risks and losses and ensuring operational continuity and safety