Introduction
Direct current (DC) systems are a fundamental part of modern electrical and electronic applications. Unlike alternating current (AC), where the current periodically reverses direction, DC maintains a constant flow in one direction. This makes it particularly useful for devices and systems that require a stable and reliable power supply. From batteries and solar panels to electric vehicles and industrial automation, DC power plays a crucial role in various fields.
This article explores the characteristics of DC systems, different methods for generating DC power, and their applications. Understanding these aspects can help in optimizing the selection and usage of DC power for different needs.

Key Characteristics of DC Systems
DC power offers several essential characteristics that make it suitable for a wide range of applications.
1. Constant Direction
- In a DC system, electric charges move in a single direction, typically from the positive terminal to the negative terminal.
- This unidirectional flow ensures a stable power supply, which is critical for electronic devices and circuits.
2. Stable Magnitude
- The intensity or amplitude of DC remains constant over time in an ideal scenario.
- Unlike AC, where the current varies sinusoidally, DC provides a continuous and predictable energy flow.
- This stability is particularly beneficial for applications where fluctuations in power could cause malfunctions or inefficiencies.
3. Constant Voltage
- The voltage in a DC system remains steady without significant variations, making it ideal for sensitive electronics.
- A stable voltage supply prevents issues like voltage drops or spikes, which could damage components in electronic circuits.
Methods of Generating DC Power
Several methods are used to generate direct current, each with its own advantages and suitable applications.
1. Batteries
- Batteries are one of the most common sources of DC power.
- Examples include dry cells, lead-acid batteries, and lithium-ion batteries.
- They store chemical energy and convert it into electrical energy when connected to a circuit.
- Batteries are widely used in portable electronics, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and backup power systems.
2. DC Generators
- DC generators convert mechanical energy into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction.
- They consist of a rotor (moving part) and a stator (stationary part).
- When the rotor spins within a magnetic field, it induces a direct current in the windings.
- These generators are used in industrial applications, renewable energy systems, and emergency power supply units.
3. Rectifiers
- Rectifiers are devices that convert AC to DC using diodes or other semiconductor components.
- They allow the current to flow in only one direction, filtering out the reverse polarity cycles of AC power.
- Rectifiers are found in power adapters, battery chargers, and electronic power supplies.
Applications of DC Systems
DC power is widely used in multiple industries, from consumer electronics to renewable energy and industrial automation.
1. Electronic Devices
- Most modern electronic devices, such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets, operate on DC power.
- These devices rely on batteries as their primary power source and are often charged using rectified AC from wall outlets.
- DC power ensures the consistent and reliable operation of these gadgets.
2. Electric Vehicles (EVs)
- Electric vehicles are powered by DC energy stored in battery packs.
- The DC battery supplies power to the vehicle’s electric motor, which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy for movement.
- During charging, the onboard charger converts AC from the power grid into DC to recharge the battery.
- High-speed charging stations provide direct DC charging, allowing for faster energy replenishment.
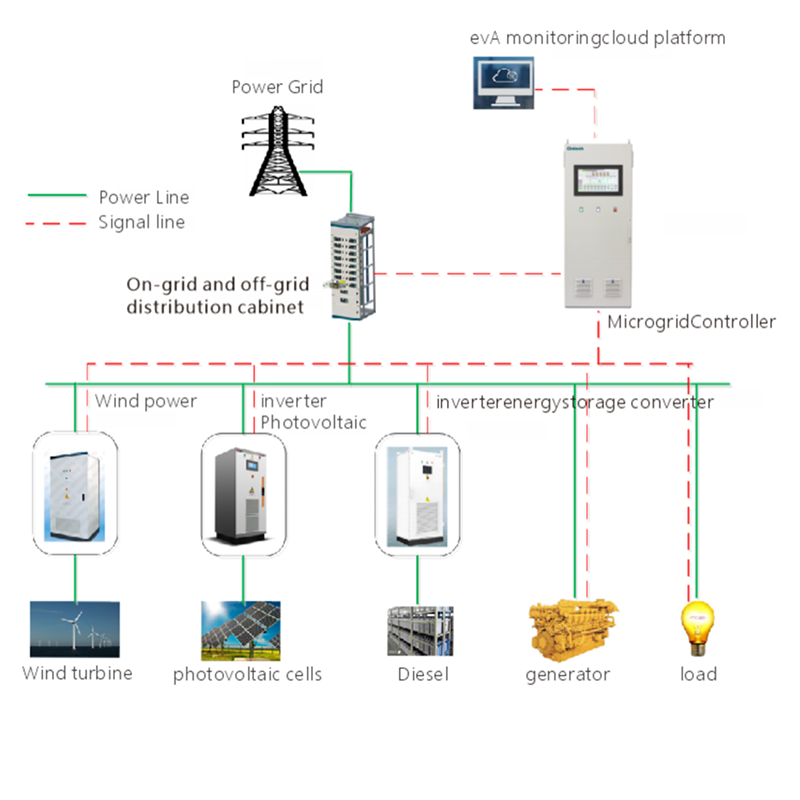
3. Solar Power Generation
- Solar panels generate DC electricity by converting sunlight into electrical energy through photovoltaic (PV) cells.
- The generated DC power can be stored in batteries for later use or converted to AC through an inverter for powering homes and businesses.
- Solar energy systems rely heavily on DC power for energy storage and distribution, making them essential for renewable energy solutions.
4. Industrial Control Systems
- Many industrial automation systems depend on low-voltage DC power to operate efficiently.
- Devices such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs), sensors, and actuators require stable DC power to function properly.
- These components are used in manufacturing, logistics, and automation to enhance precision, reliability, and efficiency.
The Future of DC Systems
As technology continues to evolve, DC power systems are expected to become even more efficient, intelligent, and environmentally friendly. Innovations in energy conversion, power management, and sustainability practices are driving the next generation of DC power solutions.
- Improved Energy Efficiency: Advances in semiconductor technology are enabling more efficient rectifiers and power supplies, reducing energy loss during AC-to-DC conversion.
- Smart Power Management: The integration of AI and IoT in power systems allows for better monitoring and optimization of DC energy usage.
- Sustainable Practices: The increasing adoption of solar energy and battery storage solutions is reinforcing the importance of DC power in reducing carbon footprints and promoting green energy.
Conclusion
DC systems play an indispensable role in modern technology, providing stable and efficient power for various applications. Understanding the characteristics of DC power, different methods of generation, and its applications can help users optimize its use in electronic devices, electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and industrial automation.
With continuous advancements in power technology, DC systems are set to become even more integral to future energy solutions. By choosing the right DC power sources and implementing efficient energy management techniques, businesses and individuals can improve reliability, efficiency, and sustainability in their operations.