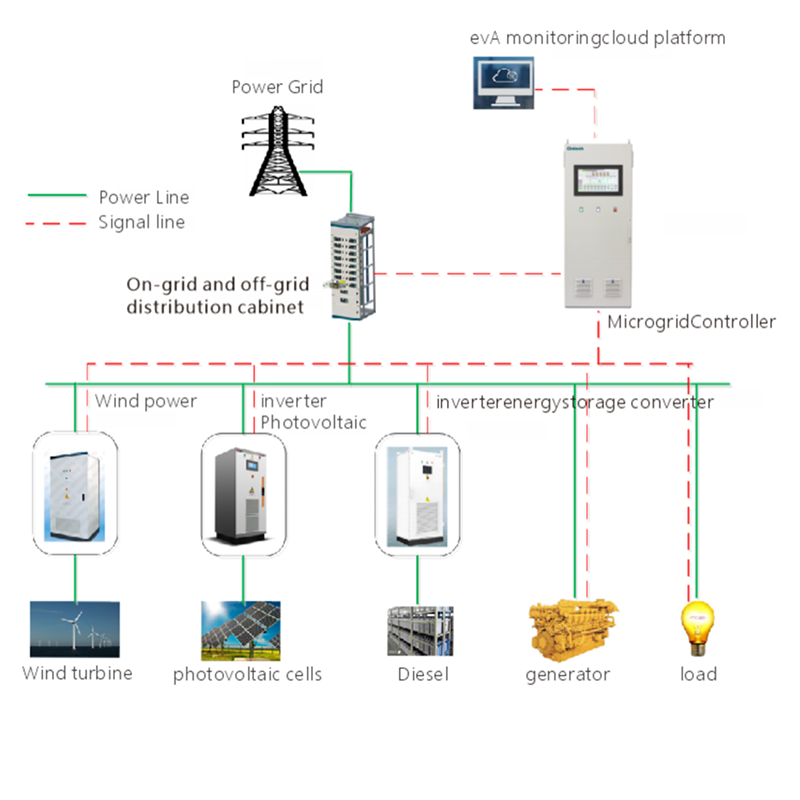
The definition of a DC power supply system
A DC Power Supply System is designed to provide a stable and reliable source of direct current (DC) for various applications. These systems are critical in numerous industries, including telecommunications, data centers, industrial automation, renewable energy, and more. Below, we explore the components, types, applications, and considerations for designing and implementing DC power supply systems.
 Components of a DC Power Supply System:
Components of a DC Power Supply System:
Rectifiers:
Function: Convert AC (alternating current) from the grid or other sources into DC.
Types: Single-phase and three-phase rectifiers, switch-mode power supplies (SMPS).
Features: High efficiency, low ripple, and advanced control capabilities.
Batteries:
Function: Store electrical energy to provide backup power during outages.
Types: Lead-acid, lithium-ion, nickel-cadmium, etc.
Considerations: Capacity (Ah), cycle life, charge/discharge rates, and environmental impact.
Distribution Units (PDUs):
Function: Distribute DC power to various loads within the system.
Components: Circuit breakers, fuses, connectors, and monitoring devices.
Features: Modular design, hot-swappable components, and remote monitoring capabilities.
Battery Management Systems (BMS):
Function: Monitor and manage battery health, ensuring safe operation and optimal performance.
Features: Overcharge/overdischarge protection, temperature monitoring, cell balancing, and diagnostics.
Inverters (Optional):
Function: Convert DC back to AC for applications requiring alternating current.
Types: Pure sine wave inverters, modified sine wave inverters.
Applications: Backup power systems, renewable energy integration.
Monitoring and Control Systems:
Function: Provide real-time monitoring and control of the entire system.
Features: Remote access, data logging, alarms, and automated decision-making.
Thermal Management:
Function: Maintain optimal operating temperatures for all components.
Components: Fans, heat sinks, liquid cooling systems.
Considerations: Energy efficiency, noise levels, and reliability.
Types of DC Power Supply Systems:
Telecommunications Power Systems:
Application: Powering telecom infrastructure such as base stations, data centers, and network equipment.
Features: High reliability, redundancy, and scalability.
Example: 48V DC systems are commonly used in telecom networks.
Data Center Power Systems:
Application: Providing uninterrupted power to servers, storage devices, and networking equipment.
Features: High efficiency, modular design, and integrated UPS (uninterruptible power supply) systems.
Example: Rack-mounted DC power supplies with integrated battery backup.
Industrial Automation Power Systems:
Application: Powering PLCs (programmable logic controllers), sensors, actuators, and motor drives in manufacturing environments.
Features: Robust design, high current capacity, and integrated protection mechanisms.
Example: 24V DC systems are widely used in industrial automation.
Renewable Energy Power Systems:
Application: Storing and managing energy generated by solar panels, wind turbines, and other renewable sources.
Features: Battery storage, charge controllers, and grid-tie inverters.
Example: Off-grid solar power systems with battery banks and MPPT (maximum power point tracking) controllers.
Transportation Power Systems:
Application: Powering electric vehicles, trains, and other transportation systems.
Features: High energy density, fast charging capabilities, and safety features.
Example: Lithium-ion battery packs in electric buses and trains.
Medical Equipment Power Systems:
Application: Ensuring reliable power for medical devices and diagnostic equipment.
Features: High precision, low noise, and backup power capabilities.
Example: Isolated DC power supplies for sensitive medical instruments.
Applications of DC Power Supply Systems:
Telecommunications:
Usage: Powering base stations, routers, switches, and other network infrastructure.
Benefits: High availability, redundancy, and energy efficiency.
Data Centers:
Usage: Providing reliable power to servers, storage devices, and networking equipment.
Benefits: Uninterrupted power supply, energy savings, and scalability.
Industrial Automation:
Usage: Driving motors, actuators, and sensors in manufacturing processes.
Benefits: High current capacity, robust design, and integrated protection.
Renewable Energy:
Usage: Storing and distributing energy from solar panels and wind turbines.
Benefits: Sustainable energy management, grid stability, and off-grid capability.
Transportation:
Usage: Powering electric vehicles, trains, and other transportation systems.
Benefits: Reduced emissions, fast charging, and long-range capability.
Medical Facilities:
Usage: Ensuring continuous power for critical medical equipment.
Benefits: High reliability, low noise, and backup power.
Military and Aerospace:
Usage: Powering avionics, radar systems, and communication equipment.
Benefits: High reliability, compact design, and rugged construction.
Design Considerations for DC Power Supply Systems:
Voltage Levels:
Standard Voltages: Commonly used voltages include 12V, 24V, 48V, and higher for specialized applications.
Selection Criteria: Based on load requirements, efficiency, and safety standards.
Current Capacity:
Determine Load Requirements: Calculate the total current needed by all connected devices.
Scalability: Ensure the system can handle future increases in demand.
Redundancy and Reliability:
N+1 Redundancy: Include one extra unit to ensure continuous operation if one fails.
Hot-Swappable Components: Allow for maintenance without shutting down the system.
Efficiency and Thermal Management:
Energy Efficiency: Optimize the system to minimize energy losses and reduce operational costs.
Cooling Solutions: Implement effective cooling strategies to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
Safety and Protection:
Overcurrent Protection: Use fuses and circuit breakers to protect against excessive currents.
Short Circuit Protection: Prevent damage from short circuits and ensure safe operation.
Grounding and Isolation: Proper grounding and isolation are required to prevent electrical hazards.
Monitoring and Maintenance:
Remote Monitoring: Implement systems for real-time monitoring and alerts.
Regular Maintenance: Schedule routine checks and maintenance to ensure long-term reliability.
Example Scenarios:
Telecommunications Base Station:
A telecommunications company uses a 48V DC power supply system to power its base station. The system includes rectifiers, batteries, and PDUs. During power outages, the batteries provide backup power, ensuring continuous service. Advanced BMS ensures optimal battery performance and longevity.
Data Center:
A data center employs a rack-mounted DC power supply system with integrated battery backup. The system powers servers, storage devices, and networking equipment. High-efficiency rectifiers and modular design allow for easy expansion and maintenance. Remote monitoring ensures proactive management of the power infrastructure.
Solar Power System:
An off-grid solar power system uses a DC power supply system with MPPT charge controllers and battery storage. The system stores energy generated by solar panels during the day and distributes it to household appliances and lighting at night. Inverters convert DC to AC for compatibility with standard household devices.
Electric Bus Charging Station:
An electric bus charging station utilizes a high-capacity DC power supply system to quickly charge buses during stops. Fast-charging technology and robust thermal management ensure efficient and reliable operation. Redundant power supplies provide backup in case of failure.
Summary
A DC Power Supply System is essential for providing stable and reliable power across various applications, from telecommunications and data centers to industrial automation, renewable energy, and transportation. By carefully selecting components, Ontech designs for redundancy and scalability, and implementing advanced monitoring and protection mechanisms, these systems ensure high availability and efficiency. Whether powering critical infrastructure or supporting sustainable energy solutions, DC power supply systems play a crucial role in modern technological ecosystems.