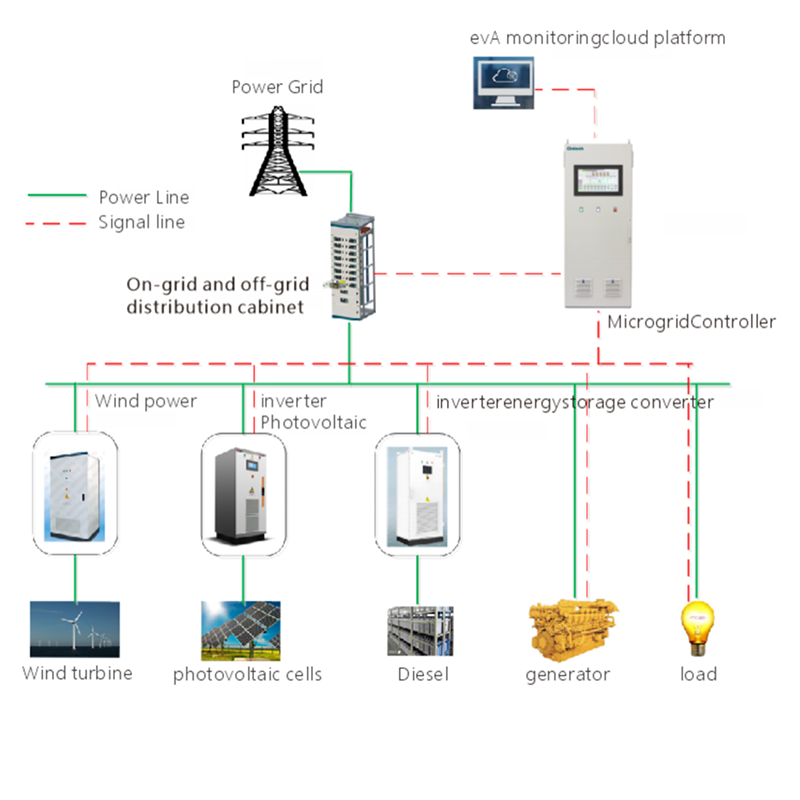
Portable Power Storage refers to compact, mobile energy storage devices designed to provide power on the go. These systems are essential for outdoor activities, emergency preparedness, and situations where access to conventional power sources is limited or unavailable. They range from small personal power banks to larger portable power stations capable of powering various devices and appliances.

Key Features of Portable Power Storage
Battery Technology:
Types: Lithium-ion, Lithium-polymer, Lead-acid, and other emerging technologies like solid-state batteries.
Characteristics: Energy density, weight, cycle life, safety, and environmental impact vary by type.
Applications: Personal electronics, camping gear, medical equipment, construction tools, etc.
Capacity and Output:
Capacity: Measured in watt-hours (Wh) or ampere-hours (Ah), indicating how much energy the device can store.
Output Ports: Include USB ports (Type-A, Type-C), AC outlets, DC ports (cigarette lighter socket), and sometimes specialized connectors for specific devices.
Power Ratings: Indicate the maximum power output the device can deliver, often ranging from a few watts for small gadgets to several hundred watts for larger appliances.
Portability:
Size and Weight: Designed to be lightweight and compact for easy transportation.
Handles and Wheels: Some models include ergonomic handles or wheels for easier mobility.
Durability: Built to withstand outdoor conditions with rugged casings and weather-resistant features.
Charging Methods:
Solar Charging: Many portable power stations offer solar panel compatibility for renewable energy charging.
AC Charging: Standard wall outlet charging for home or office use.
Car Charging: Cigarette lighter socket adapters for charging while driving.
Fast Charging: Some units support fast charging technologies to minimize downtime.
Safety Features:
Battery Management System (BMS): Monitors battery health, prevents overcharging, and ensures safe operation.
Short Circuit Protection: Prevents damage from electrical faults.
Temperature Control: Includes thermal management systems to prevent overheating.
User Interface and Monitoring:
Display Screens: Provide real-time information on battery level, input/output status, and remaining runtime.
Mobile Apps: Some models offer companion apps for remote monitoring and control via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
Types of Portable Power Storage:
Power Banks:
Usage: Charge smartphones, tablets, and other small electronic devices.
Capacity: Typically ranges from 5,000 mAh to 30,000 mAh.
Features: Compact size, multiple USB ports, and sometimes wireless charging capabilities.
Portable Power Stations
Usage: Power larger devices such as laptops, mini-fridges, power tools, and even some household appliances.
Capacity: Ranges from 100 Wh to over 2,000 Wh.
Features: Multiple output ports (USB, AC, DC), built-in inverters, and often solar panel compatibility.
Solar Generators:
Usage: Combine a portable power station with integrated or external solar panels for off-grid energy generation.
Capacity: Similar to portable power stations but optimized for renewable energy input.
Features: Solar panel compatibility, high-efficiency charge controllers, and eco-friendly design.
Applications of Portable Power Storage
Outdoor Activities:
Usage: Camping, hiking, fishing, and other outdoor adventures.
Benefits: Provides reliable power for lighting, cooking, communication devices, and entertainment.
Emergency Preparedness:
Usage: Backup power during outages, natural disasters, or emergencies.
Benefits: Ensures critical devices like medical equipment, communication devices, and lighting remain operational.
Construction and Work Sites:
Usage: Power tools, lights, and other equipment at remote job sites without access to grid power.
Benefits: Enhances productivity and safety by providing a consistent power source.
Travel and Road Trips:
Usage: Charge devices while traveling, especially in areas without convenient access to power outlets.
Benefits: Keeps devices powered and functional, ensuring connectivity and convenience.
Off-Grid Living:
Usage: Support sustainable living in remote locations without grid access.
Benefits: Enables the use of modern conveniences and technology while minimizing reliance on traditional power sources.
Example Scenarios:
Camping Trip:
A family uses a portable power station to charge their phones, run a portable fridge, and power LED lights during a weekend camping trip. The station also includes a solar panel for continuous charging during daylight hours.
Emergency Outage:
During a power outage caused by severe weather, a homeowner relies on a portable power station to keep their refrigerator running, charge their phone, and power a radio for updates. The station’s long-lasting battery provides peace of mind until the grid is restored.
Remote Construction Site:
Workers at a remote construction site use a portable power station to operate power tools, charge cordless drills, and illuminate the work area after dark. The station’s robust build and multiple output options make it ideal for demanding environments.
Road Trip:
Travelers use a power bank to charge their devices while driving through rural areas with limited access to charging stations. The power bank’s compact size and high capacity ensure they stay connected throughout their journey.
Summary
Portable power storage offers versatile solutions for powering devices and appliances in various settings, from outdoor adventures to emergencies. By leveraging advanced battery technologies and multiple charging methods, these devices enhance convenience, reliability, and sustainability. Whether you need a small power bank for personal electronics or a large portable power station for more demanding applications, there is a portable power solution tailored to meet your needs.