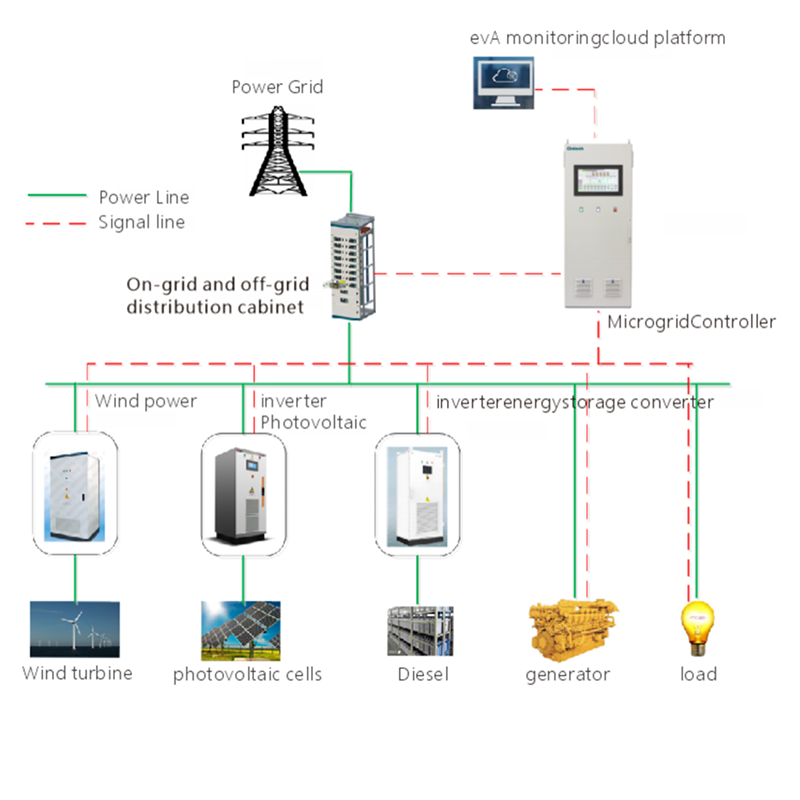
A microgrid system is a small-scale power network that can operate independently or in conjunction with the main grid. It typically consists of distributed energy resources (DERs), energy storage devices, loads, and control systems. Microgrids enhance power supply reliability, promote the utilization of renewable energy, and provide backup power during main grid outages.

Main Components of a Microgrid System
- Distributed Generation
Distributed generation refers to small-scale power generation sources located close to where the energy is consumed. These sources can include both renewable and conventional energy systems.
Solar Energy: Solar photovoltaic (PV) panels that convert sunlight into electricity.
Wind Energy: Wind turbines that generate electricity from wind.
Diesel Generators: Backup generators powered by diesel fuel, typically used when other energy sources are insufficient or during peak demand periods.
- Energy Storage Systems
Energy storage systems store excess energy generated by distributed generation sources for later use, helping to balance supply and demand and improve overall reliability.
Batteries: Devices such as lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries that store electrical energy for later use.
Supercapacitors: High-capacity capacitors capable of rapid charging and discharging, suitable for short-term energy storage needs.
Flywheels: Mechanical devices that store energy in a rotating mass, providing quick response times and high power density.
- Loads
Loads represent the consumers of electricity within the microgrid, including residential, commercial, and industrial users.
Residential Loads: Households that consume electricity for lighting, heating, cooling, appliances, etc.
Commercial Loads: Businesses and offices that require electricity for operations, lighting, HVAC systems, and other equipment.
Industrial Loads: Factories and manufacturing facilities that have significant energy demands for machinery, production lines, and other processes.
- Control Systems
Control systems are essential for managing the complex interactions between different components of the microgrid. They ensure efficient operation, stability, and safety.
Energy Management System (EMS): Responsible for optimizing the dispatch and operation of energy resources within the microgrid. It balances energy generation, storage, and consumption to meet demand efficiently.
Protection and Control Systems: Ensure the safe and stable operation of the microgrid by monitoring and controlling various parameters such as voltage, frequency, and power flow. These systems prevent failures and enhance reliability.
Application Scenarios
Remote Areas: Addressing issues of no electricity or unstable power supply.
Urban Areas: Enhancing power supply reliability and energy efficiency.
Industrial Parks: Meeting high reliability demands and reducing electricity costs.
Microgrids, as a modern, resilient, and sustainable energy solution, integrate distributed energy resources, energy storage systems, loads, and advanced control systems. They not only enhance power supply reliability but also promote the widespread adoption of renewable energy. Their flexible operational modes enable efficient performance under various conditions, making them a critical component of future energy systems. Whether addressing emergencies or achieving long-term sustainable development goals, microgrids demonstrate significant potential and application prospects.