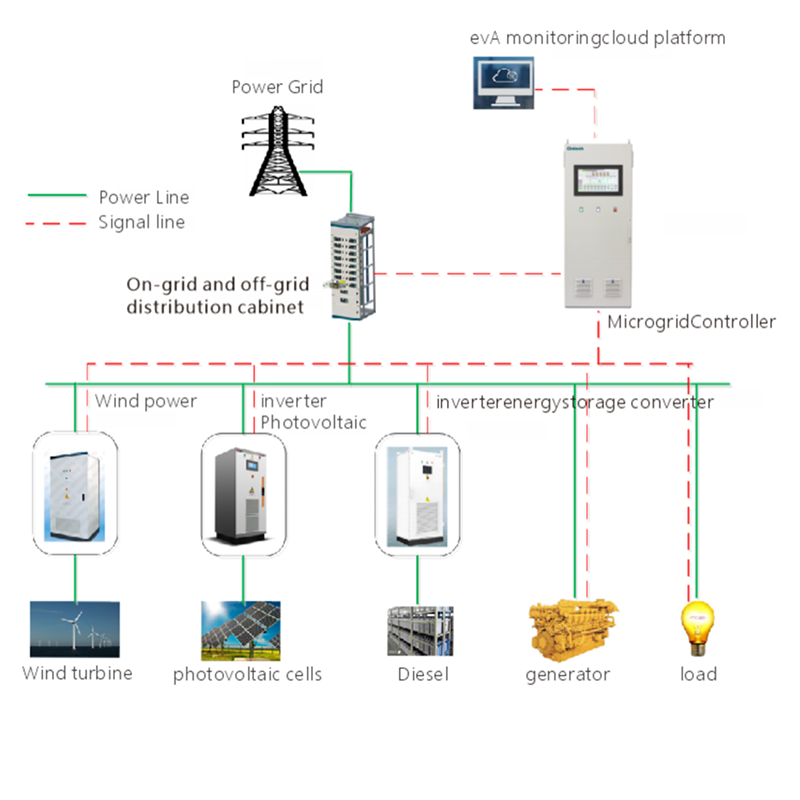
AC Power Backup refers to providing continuous alternating current (AC) power to critical equipment during power supply interruptions or instability. This backup system ensures that essential devices and operations remain functional even when the primary power source fails or becomes unreliable. AC power backup systems are widely used in environments where uninterrupted power is crucial, such as data centers, hospitals, communication base stations, and industrial production facilities.
Core Components of AC Power Backup Systems
AC power backup systems are crucial for maintaining continuous operation during power outages or instability. Below are the core components that make up these systems:
- Backup Power Sources:
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS):
Purpose: Provides short-term power during brief outages or voltage fluctuations, ensuring critical equipment remains operational.
- Online UPS: Continuously converts incoming AC power to DC and then back to AC, providing clean power and immediate backup in case of an outage.
- Offline (Standby) UPS: Switches to battery power when the main supply fails, with a slight delay.
- Line-Interactive UPS: Similar to offline, but includes automatic voltage regulation to handle minor power fluctuations without switching to battery.
- Generators (Diesel or Natural Gas): Provide long-term power during extended outages, ensuring continuous operation for hours or days.
- Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS):
Purpose: Automatically switch between the primary power source and the backup power source when the primary source fails.
Functionality: Ensures seamless transition to the backup power source, minimizing downtime and maintaining continuous power supply to critical loads.
- Battery Banks:
Purpose: Store electrical energy for UPS systems to use during power outages.
Usage: Batteries discharge stored energy to provide power to connected devices until either the main power is restored or the generator takes over.
Considerations: Battery capacity and lifespan are key factors in determining how long the UPS can support the load.
- Monitoring and Management Systems:
Purpose: Real-time monitoring of the status of both primary and backup power sources.
Features:
Alerts: Provide notifications for any issues or changes in power status.
Management: Enable remote management and control of the backup system.
Data Logging: Track historical performance and usage data for analysis and optimization.
Benefits: Enhances the reliability and efficiency of the backup system by ensuring prompt responses to potential problems.
Summary of Core Components:
Backup Power Sources:
UPS: Provides short-term power during brief outages or voltage fluctuations.
Types: Online, Offline, Line-Interactive.
Generators: These offer long-term power during extended outages, typically diesel or natural gas.
Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS):
Automatically switches to backup power when the primary source fails, ensuring continuous power supply.
Battery Banks:
Store energy for UPS systems, providing power during outages until the generator starts or main power is restored.
Monitoring and Management Systems:
Monitor power status in real time, provide alerts, and enable remote management for enhanced reliability and efficiency.
Applications of AC Power Backup Systems
AC power backup systems are essential for ensuring continuous operation and preventing disruptions in various critical environments. Below are detailed descriptions of the primary application scenarios:
- Data Centers:
Purpose: Ensure that servers, storage systems, and network equipment remain operational during power outages to prevent data loss and service interruptions.
Importance:
Continuous Operation: Data centers must maintain uptime to support business operations, cloud services, and other critical applications.
Data Integrity: Prevents corruption or loss of data due to unexpected power failures.
Redundancy: Multiple layers of backup (e.g., UPS, generators) ensure high availability and reliability.
- Hospitals:
Purpose: Provide uninterrupted power to life-support systems, diagnostic equipment, and other medical devices to ensure patient safety and care.
Importance:
Life-Support Systems: Critical for patients relying on ventilators, monitors, and other life-saving equipment.
Diagnostic Equipment: Ensures that imaging machines, laboratory equipment, and other diagnostics continue functioning without interruption.
Emergency Services: Supports emergency rooms, operating theaters, and other critical areas that require constant power.
- Communication Base Stations:
Purpose: Ensure the continuity of communication networks, maintaining connectivity and services, especially during emergencies.
Importance:
Network Continuity: Keeps mobile networks, internet services, and emergency communications operational.
Disaster Recovery: Provides reliable communication channels during natural disasters or other crises when primary power may be disrupted.
Remote Areas: Ensure coverage in remote or underserved areas where power outages can be more frequent.
- Industrial Production:
Purpose: Prevent production lines from stopping due to power outages, minimizing downtime and reducing financial losses.
Importance:
Process Continuity: Maintains the operation of machinery and processes that cannot afford to stop abruptly, such as manufacturing plants, refineries, and chemical processing facilities.
Safety: Ensures that safety systems and controls remain functional, preventing accidents and hazardous situations.
Cost Efficiency: Reducing the costs associated with restarting complex processes and recovering from unplanned downtime.
- Homes and Offices:
Purpose: Provide short-term power support to critical devices like computers, routers, and security systems during brief outages.
Importance:
Business Continuity: Allows employees to continue working on critical tasks without disruption.
Home Safety: Keeps essential home devices running, such as security systems, refrigerators, and lighting.
Convenience: Prevents data loss and inconvenience caused by sudden power cuts, ensuring smooth daily operations.
Summary of Application Scenarios:
Data Centers:
Ensure continuous operation of servers and network equipment, preventing data loss and service interruptions.
Hospitals:
Provide uninterrupted power to life-support systems and diagnostic equipment, ensuring patient safety and care.
Communication Base Stations:
Maintain network continuity, supporting emergency communications and general connectivity during outages.
Industrial Production:
Prevent production line interruptions, ensuring process continuity and safety while minimizing financial losses.
Homes and Offices:
Offer short-term power support to critical devices, ensuring business continuity and home safety.
Conclusion
AC power backup systems play a crucial role in maintaining continuous operation across a variety of settings, from large-scale industrial facilities and critical infrastructure to homes and offices. By providing reliable and uninterrupted power, these systems enhance the resilience and dependability of operations, ensuring that essential functions can continue even in the face of power supply disruptions.