As the popularity and demand for sustainable energy are increasing daily, understanding the key differences between a grid and a microgrid is crucial. Although both systems work in distributing electric currents, they vary significantly in operations, structure, and benefits. In this article, we will explore the key differences between a traditional grid and a microgrid, with the benefits of using the microgrid system.

The Key Differences Between A Grid And A Microgrid
Definition And Scale
Grid is referred to as the main grid or central grid, it is a network of power generation, transmission, and distribution systems that supplies electricity in large quantities of regions, cities, states, and a country. The system relies on centralized power plants and transmissions for longer distances.
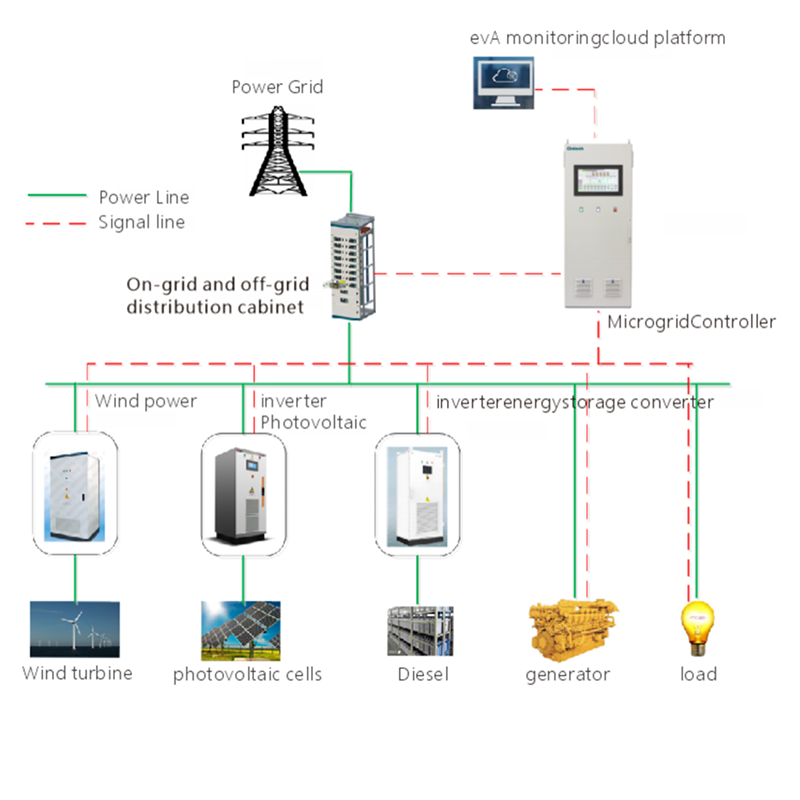
A microgrid is a local energy system that operates either independently or in conjunction with the main grid. It is mostly used in fewer areas like the university campus, a residential community, or an industrial facility.
Energy Independence
The traditional grid is supplied by centralized power plants, which can be affected by failures in the transmission lines or extreme weather events. On the other hand, microgrids with their energy sources, solar panels or wind turbines and with energy storage batteries can function by themselves, thus, Sure to have a power supply even during grid failures.
Energy Storage And Management
The main grid does not have sufficient energy storage systems but rather constantly balances the real-time supply with the demand. Microgrids, through high-capacity storage batteries, are more likely to store excess energy produced during off-peak periods for use during peak periods when the grid is congested or outages occur and thus are more effective and resilient.
The main grid often lacks substantial energy storage systems, relying instead on balancing real-time supply and demand.
Microgrids frequently integrate storage batteries, which are able to balance their solar and wind energy and are able to store excessive energy for utilization during peak hours or blackouts, resulting in more efficient and resilient microgrids.
Flexibility and Control
The grids are obliged to various users remembering that the energy used for many purposes is not flexible thus the energy is put to various uses. Users are given greater control over energy consumption and the level of consumption is optimized at the microgrid level by using microgrid technology to integrate distributed energy generation, energy storage, and control loads so that the maximum results will be achieved.
Grids serve diverse users and have limited flexibility in customizing energy delivery for specific needs.
Microgrids have a higher degree of control and energy distribution, so the consumer can have better energy efficiency by using smart appliances and other related technologies, and the energy can be provided by renewable sources and can be utilized in a specific order to allow the other functions to continue.
Environmental Impact
The primary central grid is mostly powered by fossil fuels and this is what causes more carbon emissions which are then causing the environmental problems. However, microgrids provide the integration of renewable energy sources and battery storage management which gives rise to the decrease of non-renewable resources and a push for sustainability. Mostly we have to use fossil fuels in the central grid which causes carbon emissions and environmental threats.
Much of the time, the microgrids get the inclusions of renewable energy sources and energy storage batteries leading to the breaking of the non-renewable resources and the development of sustainability.
The Benefits of Microgrids
Enhanced Reliability
The current status of the energy distribution grid can be a disappointment when energy is not widely available or it is subjected to disasters. In addition, microgrids with storage batteries can be integrated and in case of a blackout, collect and distribute power from alternative sources.
The present-day energy distribution grid falls short when it comes to energy accessibility and is prone to calamities like natural disasters and breakdowns. There are solutions such as microgrids that can supply electricity coming from renewable energy sources to consumers. Together with energy storage batteries, microgrids can convert and absorb energy from elsewhere when the main grid is non-existent.
Energy Efficiency
Microgrids have a great advantage here in terms of energy decentralization by generating electricity on-site and minimizing transportation losses. Also, in case of an energy shortage, the surplus energy generated by the solar panels can be stored in batteries and utilized later when required.
The power to distribute a part of electricity produced using the wind turbine from the local farm to the end users without loss of it is farfetched considering the grid reliability around the areas affected by storms and grid failures. Equipped with energy storage batteries, they can function autonomously, capturing and distributing energy from the core grid in the absence of the main grid.
Cost Savings
Through the use of local renewable sources and the forecasting of energy consumption and the exact amount to be used so that the costs are minimal, microgrids will help to cut energy bills. On the other hand, the technology will shield the users from the usually wild and outrageous prices of power on the main grid.
In the same vein, microgrids have positive impacts on the economy, where local industries are encouraged to install their own systems, which, in turn, reduce the costs of energy from distant areas. The combined heat and power plants also sell any excess electricity produced after the energy management system slightly refrains use by the batteries.
Sustainability
Microgrids are the leading revolution in distribution and the search for other alternatives to safer ways of obtaining energy. Solar, wind, hydro, or other clean energy sources have become the most popular for microgrids, these clean storages are also used to distribute power from sun panels to households and later on to the utility during off-peak hours.
The utilization of renewable energy sources, namely solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, is the way to go if we want our microgrids to be eco-friendly. Moreover, energy storage batteries help save energy through the use of sustainable methods.
Energy Security
Microgrids minimize dependence on centralized systems, promoting energy security for users. This fact is particularly essential in areas that are located far away from the main grid and also when it comes to mission-critical facilities like hospitals and data centers.
Microgrids reduce dependence on centralized systems and, hence, enhance energy security for users. This is of particular import for localities that are remote or facilities that are mission-critical such as hospitals and data centres.
Conclusion
The scale at which a grid and a microgrid operate, their autonomy, versatility, and energy management are the differences between the two. Microgrids are designed to run locally, harness renewable sources, and store excess energy in batteries which make them resilient and sustainable as opposed to traditional grids. If you want to get more details on these systems and energy storage solutions, you need to visit the link to Ontech Energy’s microgrid and ESS product page.